If you are considering starting a business in Oman, this guide covers every step of the process. From choosing your company structure to opening a corporate bank account, you will find the exact information needed to register your company confidently.
Oman welcomes foreign investors. Since the Foreign Capital Investment Law (FCIL) passed in 2020, entrepreneurs from any country can own 100% of their Omani company. There is no requirement for a local sponsor or Omani partner in most sectors.
We have helped more than 500 entrepreneurs from Iran, Germany, the UK, France, India, Pakistan, and other countries set up companies in Oman. This page reflects that real-world experience.

Types of Companies You Can Form in Oman
The Ministry of Commerce, Industry, and Investment Promotion (MoCIIP) recognizes several company structures. Your choice depends on the number of shareholders, your liability preference, and whether you plan to operate locally or regionally.

LLC — Limited Liability Company
The LLC is the most popular choice for foreign investors in Oman. It requires at least 2 shareholders. Each shareholder's liability is limited to their capital contribution. Personal assets remain protected.
An LLC allows 100% foreign ownership.
Best for: Medium to large businesses, partnerships, and companies with multiple investors. Many Iranian and European entrepreneurs choose this structure for trading, consulting, and logistics operations.
SPC — Single Person Company
The SPC is designed for solo entrepreneurs. A single owner controls all operations and decisions. Liability is limited to the company's investments, not your personal assets.
Like the LLC, an SPC allows 100% foreign ownership. It suits freelancers, independent consultants, and small business owners who want full control without a partner.
Best for: Solo entrepreneurs, freelancers, and one-person consultancies. Popular with professionals from India and Pakistan starting IT, marketing, or consulting firms.
Wholly Owned Subsidiary
International companies expanding into Oman can register a wholly owned subsidiary, structured as either an LLC or SPC with the parent company as the sole or majority shareholder.
Best for: Corporations from Europe, Iran, or Asia expanding their Gulf footprint.
Branch Office
A branch office allows a foreign company to operate in Oman without incorporating a separate entity. The parent company bears full liability. At least one foreign director must oversee branch operations.
Best for: Companies testing the Omani market or executing specific contracts. Common among construction firms and engineering companies from Germany, France, and the UK.
Representative Office
A representative office cannot generate profit. It exists solely for market research, promotional activities, or maintaining a brand presence — no invoicing, no contracts, no sales.
Best for: Companies conducting market feasibility studies before committing to full incorporation.
Joint Stock Company (SAOC / SAOG)
Joint stock companies suit larger businesses considering public offerings. SAOG (public) companies can list shares on the Muscat Stock Exchange. SAOC (closed) companies have a smaller shareholder base.
Best for: Large enterprises planning equity fundraising or public listings.
| Entity Type | Min. Shareholders | Foreign Ownership | Liability | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LLC | 2 | 100% | Limited | Medium–large businesses |
| SPC | 1 | 100% | Limited | Solo entrepreneurs |
| Branch Office | Parent co. | 100% | Parent liable | Market entry, contracts |
| Representative | Parent co. | 100% | Non-commercial | Market research |
| SAOC / SAOG | 2+ / 40+ | Up to 100% | Limited | Large enterprises, IPOs |
How to Register a Company in Oman: Step-by-Step
The company registration process in Oman is straightforward. With all documents ready, expect completion in 3–7 working days.
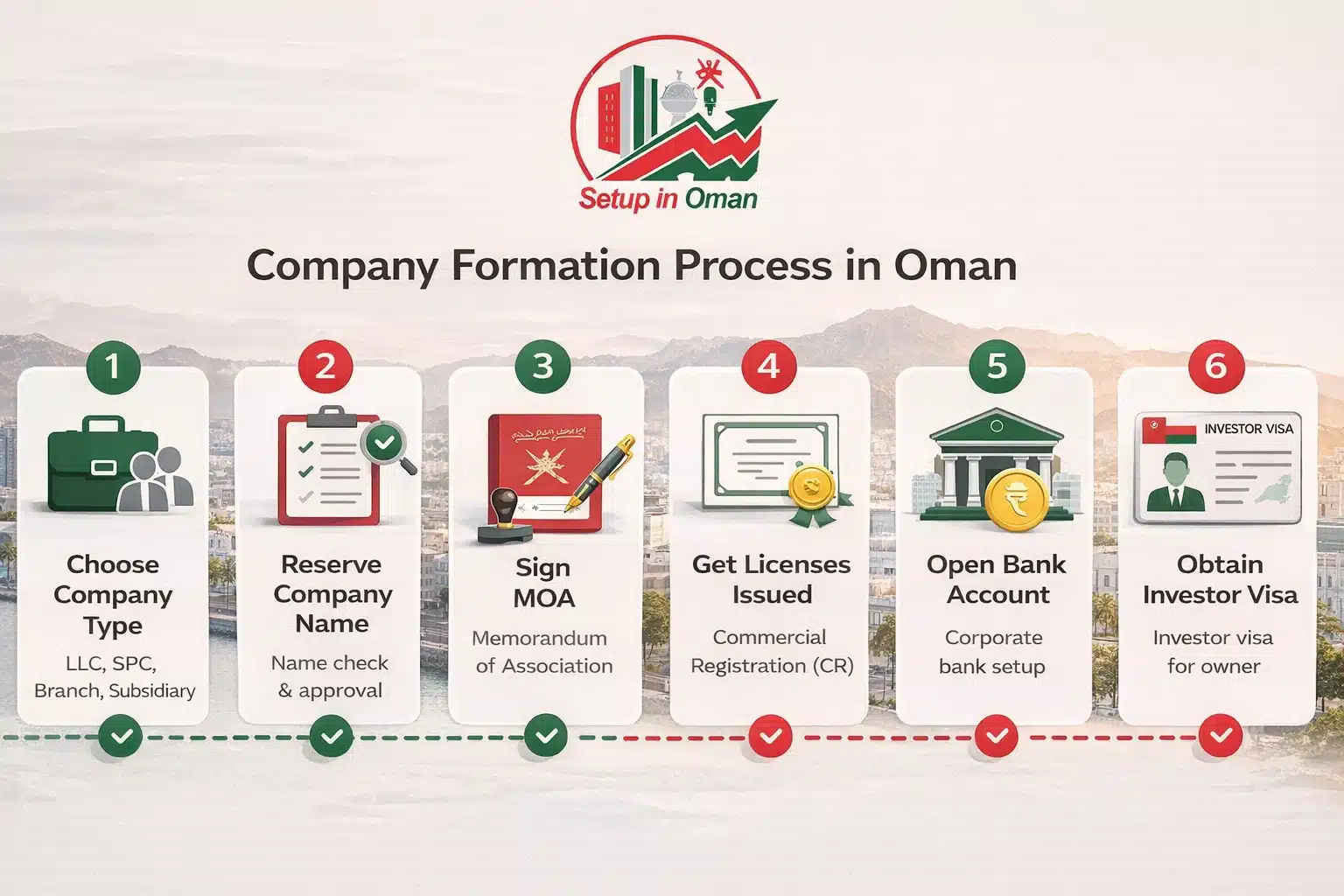
Choose Your Company Type
Decide between LLC, SPC, branch office, or subsidiary. Consider the number of shareholders, your liability preference, and whether you need an office in Oman. Our team advises you based on your specific business activity.
Time: 1 day (consultation)
Register Your Business Name
Pick three potential company names. Names must comply with MoCIIP regulations — they cannot be trademarked or identical to existing registered companies. The name must be in Arabic and can include an English translation.
Time: 1–2 days
Draft and Sign the Memorandum of Association (MOA)
The MOA includes the company name, business activities, share capital, and management structure. All shareholders sign electronically. No travel to Oman required. No notarization. No Power of Attorney needed.
Time: 1 day
Obtain Licenses and Certificates
We secure on your behalf: Investment License (1 yr), Commercial Registration / CR (3 yrs), Chamber of Commerce Membership with OCCI (1 yr), Tax Certificate (1 yr), Permit License (1 yr), and a Feasibility Report from an approved auditor.
Time: 1–2 days
Open a Corporate Bank Account
Every formation package includes a corporate bank account in OMR currency at Sohar Bank, Dhofar Bank, or National Bank of Oman.
Get Sector-Specific Licenses (If Required)
Healthcare, education, construction, food services, and financial services each require additional permits from their own regulatory authority. We handle the application for you.
A clear passport copy, your proposed company name, your preferred business activity, and any experience letter or CV that supports the chosen activity. That is it. No notarization. No travel.

Benefits of Setting Up a Company in Oman

100% Foreign Ownership — No Local Sponsor
Oman allows full foreign ownership on the mainland and in free zones. This changed in 2020 when the Foreign Capital Investment Law removed the cap that previously limited foreign ownership to 70%. German, French, British, Indian, Pakistani, and Iranian investors enjoy the same rights.
Strategic Location
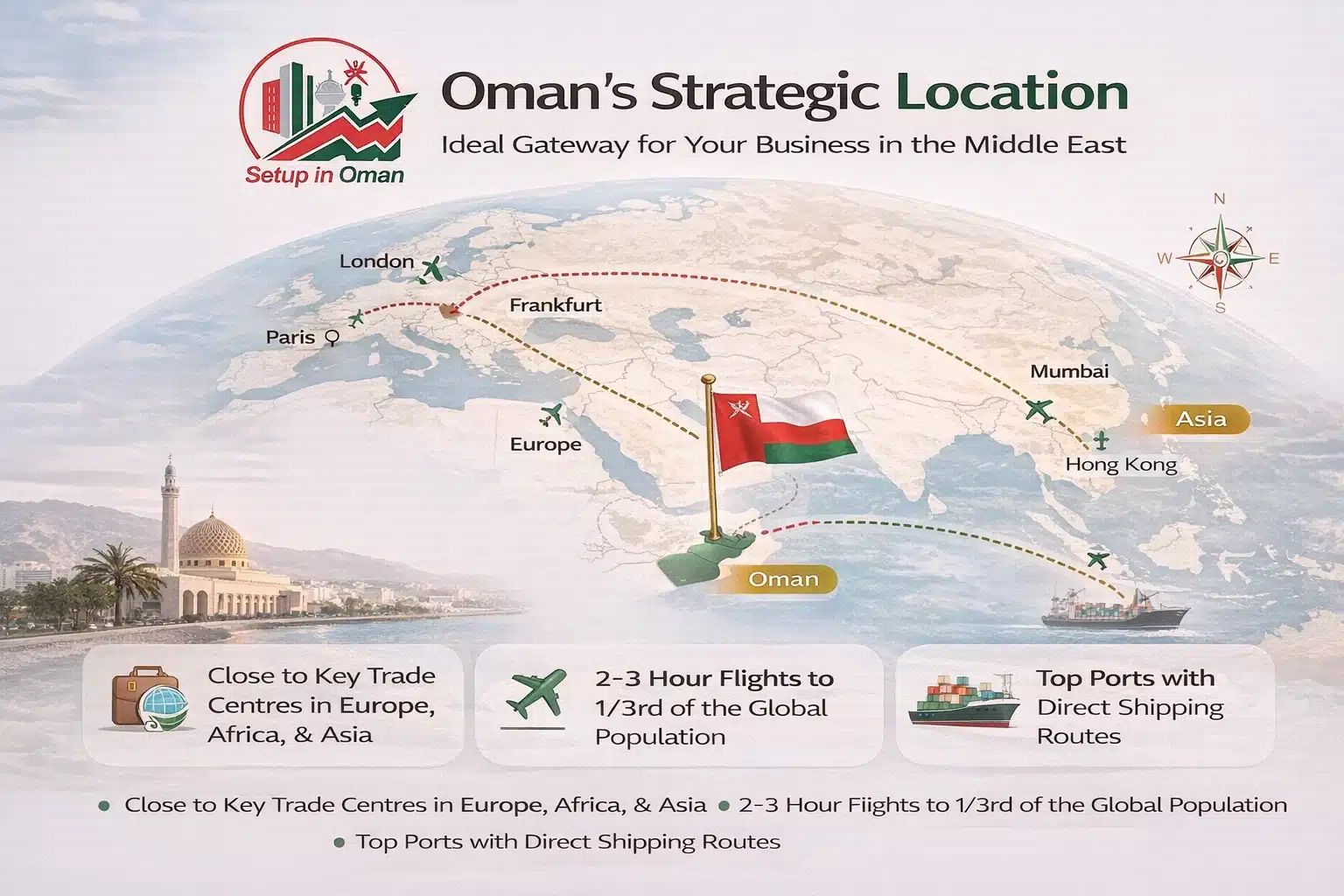
Oman sits at the mouth of the Persian Gulf. Muscat is a 90-minute flight from Dubai, a 2-hour flight from Tehran, and connects directly to Mumbai, Karachi, and major European cities.
The Sohar Free Zone and Sohar Port provide direct shipping routes to Iran, India, East Africa, and Europe — making Oman ideal for import-export, logistics, and manufacturing businesses.
Favourable Tax Regime
No personal income tax. Low corporate tax rates (3% for small businesses). Zero VAT on exports. One of the most competitive tax environments in the Gulf.
No Omanization in Year One
New companies have zero Omanization requirements during their first year. Starting year two, you hire just one Omani national. This gradual approach gives foreign businesses time to establish themselves.
Remote Registration
The entire process — name registration to license issuance — is handled electronically. Clients from Iran, Germany, the UK, France, India, and Pakistan have formed companies without ever visiting Oman.
Oman's Tax System for Companies
3% tax applies to companies with annual revenue below OMR 100,000. 15% tax applies above that threshold — still competitive against the UAE's 9% tier and far below European rates (Germany ~30%, France 25%, UK 25%).
5% VAT on domestic sales. 0% VAT on exports. No personal income tax.
| Tax Type | Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Corporate Tax (under OMR 100K) | 3% | On annual profits |
| Corporate Tax (over OMR 100K) | 15% | On annual profits |
| VAT (domestic) | 5% | Goods & services sold in Oman |
| VAT (exports) | 0% | Zero-rated |
| Personal Income Tax | 0% | Not applicable in Oman |
| Withholding Tax | 10% | On certain payments to non-residents |
Labour Laws and Omanization Requirements
Year One — No Omanization
During your first year, you have no obligation to hire Omani nationals. You can hire employees from any country — Iran, India, Pakistan, Philippines, Nepal, Bangladesh, or Europe.
Year Two and Beyond
From the second year, you need one Omani employee. As your company grows, additional Omani hires may be required depending on your industry. The Ministry of Labour sets Omanization targets by sector.
Work Permits for Foreign Employees
Hiring foreign staff requires a labour permit from the Ministry of Labour. Processing is handled through the Royal Oman Police (ROP). Read our complete work visa guide →
Working Hours & Leave
Standard workweek: 48 hours (9 hrs/day, 6 days). Employees receive a minimum of 30 calendar days of paid annual leave. Sick leave, maternity leave, and national holidays are all mandated by Omani labour law.
Oman Free Zones for Foreign Investors
Oman's free zones offer enhanced incentives: tax exemptions up to 25 years, zero customs duty on imports and re-exports, no minimum capital requirement, and full repatriation of profits and capital.
The Sohar Free Zone is particularly popular with manufacturing and logistics companies importing from Iran or India and re-exporting to Europe or Africa. Other free zones: Duqm (Special Economic Zone), Salalah Free Zone, Al Mazunah Free Zone, and Knowledge Oasis Muscat.
Company Formation in Oman vs. Other GCC Countries
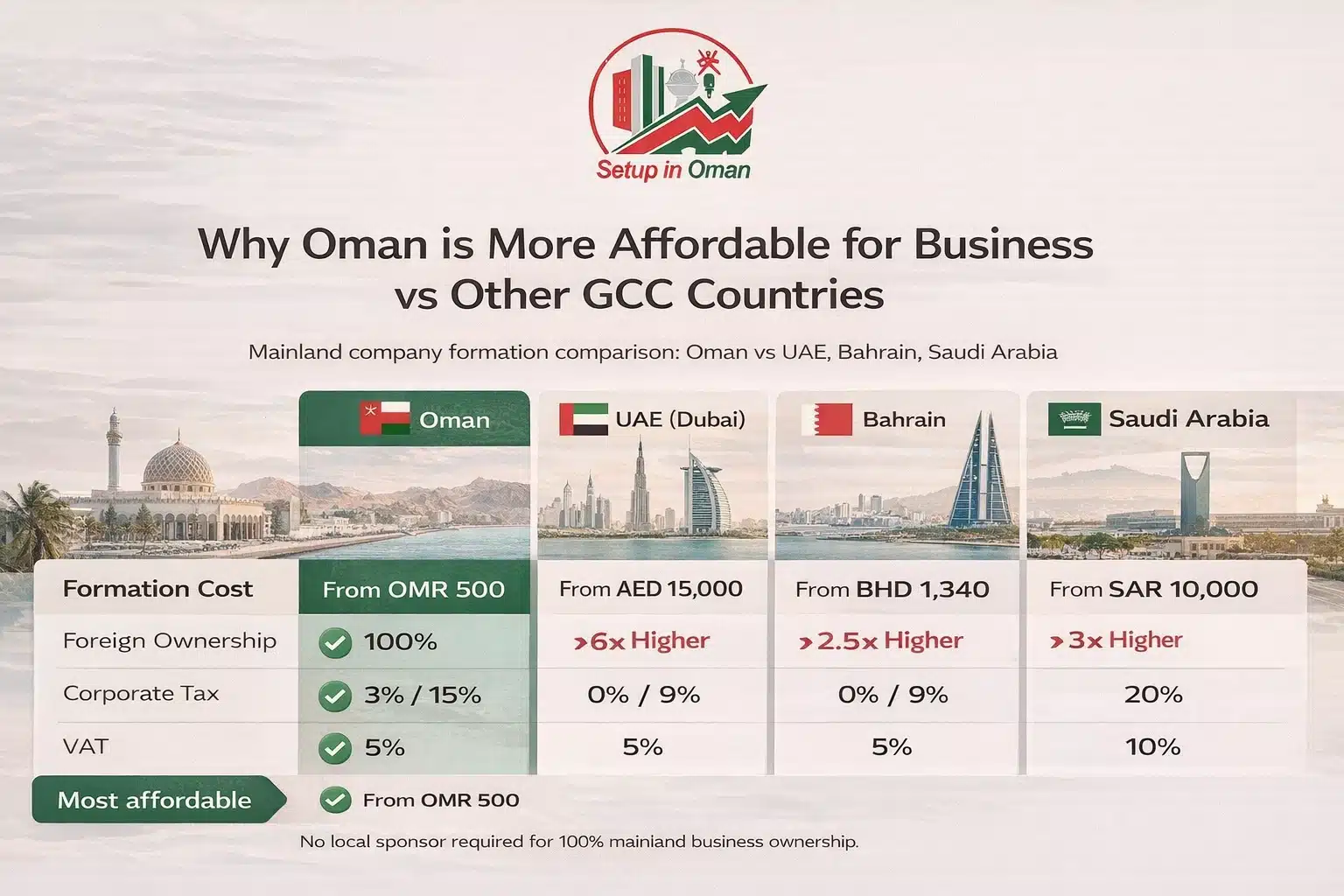
Company registration comparison across GCC countries — 2026
| Factor | Oman | UAE (Dubai) | Bahrain | Saudi Arabia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Foreign Ownership | 100% | 100% (since 2021) | 100% | 100% (most sectors) |
| Corporate Tax | 3% / 15% | 0% / 9% | 0% | 20% |
| VAT | 5% | 5% | 10% | 15% |
| Registration Time | 3–7 days | 3–10 days | 7–14 days | 5–15 days |
| Personal Income Tax | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Market Saturation | Low | High | Medium | Medium |
Oman stands out for its lower market saturation and business-friendly regulations. The 3% corporate tax rate for small businesses and zero VAT on exports make it one of the most competitive environments in the GCC.
Real Examples: Who Registers Companies in Oman?
Iranian Trading Company
A Tehran-based entrepreneur registered an LLC in Oman to import consumer goods from China and distribute them across the Gulf. Timeline: 5 working days.
German IT Consultancy
A Berlin-based software developer formed an SPC in Oman to serve clients in the Middle East. With 0% VAT on exported services and no personal income tax, the tax savings compared to Germany (30%+ effective rate) were significant.
Indian Import-Export Business
An entrepreneur from Mumbai registered an LLC in the Sohar Free Zone to import textiles from India and re-export to African markets. The free zone's customs exemptions eliminated import duties entirely.
French Consulting Firm
A Paris-based management consultancy opened a branch office in Oman to serve Omani government contracts, operating under their existing French corporate identity.
Visa Options After Company Formation
Investor Visa
The investor visa grants long-term residency in Oman. You can sponsor your spouse and dependent children. We offer two investor visa packages:
Processing time: 15–20 days. Full investor visa guide →
Work Visa for Employees
Hire foreign employees by sponsoring their work visas through a labour permit from the Ministry of Labour and visa processing through the Royal Oman Police. Full work visa guide →
License Renewal Requirements
Commercial Registration: Valid for 3 years. Renewal through MoCIIP. Investment License, Chamber of Commerce Membership, Tax Certificate, Permit License: All require annual renewal.
We offer renewal services to ensure your company stays compliant year after year. Contact us for renewal support →
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes. The 2020 Foreign Capital Investment Law allows 100% foreign ownership in most sectors on the mainland and in free zones. No local Omani partner or sponsor is required.
With all documents prepared, registration takes 3–7 working days. Name registration takes 1–2 days, MOA drafting takes 1 day, and government approvals take 1–2 days.
No. The entire process is handled remotely through MoCIIP's digital system. No travel, no notarization, no Power of Attorney required.
No. Since 2020, foreign investors can own 100% of their company without an Omani partner. Some restricted activities may require special approval, but the vast majority of business sectors are fully open.
An LLC needs at least 2 shareholders and suits partnerships or multi-investor businesses. An SPC has a single owner and suits solo entrepreneurs. Both offer limited liability and 100% foreign ownership.
3% for companies earning below OMR 100,000 per year. 15% for companies above that threshold. Exports are zero-rated for VAT. No personal income tax exists in Oman.
Yes. The registration process is fully digital. We have helped hundreds of entrepreneurs from Iran, Germany, the UK, India, and other countries register without visiting Oman.
Oman's free zones (Sohar, Duqm, Salalah, Al Mazunah) offer tax exemptions up to 25 years, zero customs duty, and full profit repatriation. They are ideal for manufacturing, logistics, and trading companies.
Zero Omanization in year one. From year two, you hire one Omani national. Requirements increase gradually based on your industry and company size.
Yes. Oman offers 100% foreign ownership, a 3% corporate tax for small businesses, zero VAT on exports, and a less saturated market than Dubai or Saudi Arabia.
5% VAT applies to goods and services sold within Oman. Exports are zero-rated (0% VAT). This significantly benefits companies with international clients.
Standard requirements include an investment license, commercial registration, chamber of commerce membership, tax certificate, and permit license. Some industries need additional sector-specific permits.
Annual renewals include the investment license, chamber of commerce membership, tax certificate, and permit license. Commercial registration renews every 3 years through MoCIIP.

